Write and Read AIMMS Data in Text Format
When two AIMMS apps communicate with each other using the same identifiers, you may want to use the text format.
Here we’ll provide a brief example of sharing persisting AIMMS data with text files.
Example description
The declaration order is as follows.
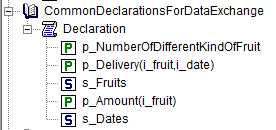
These identifiers are initialized in PostMainInitialization like this:
1Procedure PostMainInitialization {
2 Body: {
3 s_Fruits := data { orange, pear };
4 s_Dates := data { day1, day2 };
5 p_amount := data { orange:3.4567891234, pear:4.7654321987 };
6 p_delivery := data table
7 day1 day2
8 orange 1 1
9 pear 2 1 ;
10 }
11 Comment: {
12 "Add initialization statements here that require that the libraries are already initialized properly,
13 or add statements that require the Data Management module to be initialized."
14 }
The first identifier, p_NumberOfDifferentKindOfFruit, has a definition, and it not logical to write that to a text file which is also used as an input file.
So to write all identifiers in the section CommonDeclarationsForDataExchange that can also be used as input, we construct a subset of AllIdentifiers, say s_outputSet as follows:
s_outputSet := CommonDeclarationsForDataExchange * CurrentInputs ;
Writing to text file
To write the identifiers in that set to a text file, you can specify the write statement as follows:
write s_outputSet to file sp_ExchangeFilename ;
Then the output looks like this:
p_Delivery := data { ( orange, day1 ) : 1, ( orange, day2 ) : 1, ( pear, day1 ) : 2, ( pear, day2 ) : 1 } ;
s_Fruits := data { orange, pear } ;
p_Amount := data { orange : 3.457, pear : 4.765 } ;
s_Dates := data { day1, day2 } ;
Adjusting output
You may want to change the output somewhat, e.g.:
Sets are read in before they are used
Retain precision of the data
One data entry per line
You can do this by setting the options for data writing, and by using the in backup mode clause of the write statement.
More on the preferred way of setting options can be found in this article.
Thus the code becomes:
1Procedure MainExecution {
2 Body: {
3 block where
4 single_column_display := 1,
5 listing_page_width := 32000,
6 listing_number_width := 20,
7 listing_number_precision := 12 ;
8 s_outputSet := CommonDeclarationsForDataExchange * CurrentInputs ;
9 write s_outputSet
10 to file sp_ExchangeFilename
11 in backup mode ;
12 endblock ;
13 }
14}
and the output file becomes:
1s_Fruits := data
2{ orange,
3 pear } ;
4
5s_Dates := data
6{ day1,
7 day2 } ;
8
9
10p_Amount := data
11{ orange : 3.456789123400,
12 pear : 4.765432198700 } ;
13
14
15p_Delivery := data
16{ ( orange, day1 ) : 1,
17 ( orange, day2 ) : 1,
18 ( pear , day1 ) : 2,
19 ( pear , day2 ) : 1 } ;
As you can see in the above text file, the sets are filled before they are used, and the parameter data keeps its precision.
To subsequently read in that text file in another model sharing the declaration of the mentioned identifiers, you can simply do the following:
1Procedure MainExecution {
2 Body: {
3 read from file sp_ExchangeFile ;
4 }
5}
This will read in such a text file.
Example project
Both AIMMS projects can be downloaded below: