Upload and Download Files on AIMMS Cloud
This article explains how you can upload and download files to and from AIMMS PRO Storage. Please use the following project to follow this article:
Overview of AIMMS PRO Storage
AIMMS PRO Storage is a disk area managed by AIMMS PRO On-Premise and AIMMS Cloud to share files within an AIMMS application and between AIMMS applications. This disk area is separate from the disk area in which AIMMS apps are actually executing. Among other things, it handles the cases created during various (solver) sessions, which are then shared between users of the same app.
Terminology
Within AIMMS PRO Storage, folders are referred to as buckets and files are referred to as objects. When you look at the AIMMS PRO API, as presented in the AIMMS PRO UI Library, you will see the terms buckets and objects. In this article, I will use the terms folders and files.
AIMMS PRO Storage has the following folder structure, and it is best practice to follow it:
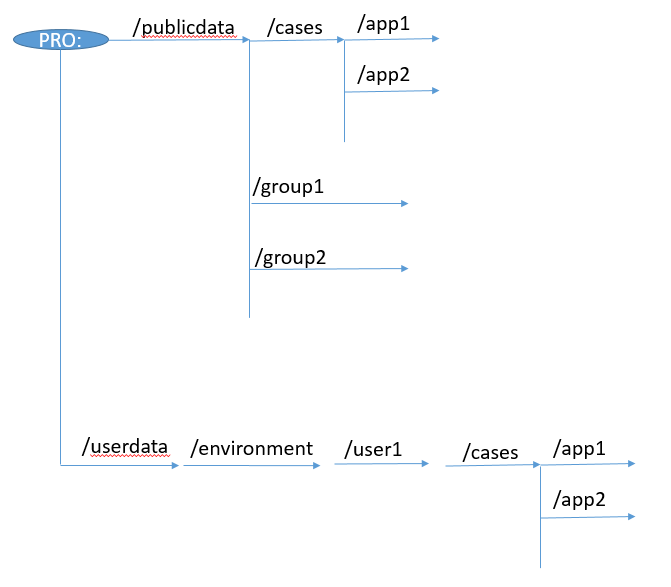
In this structure, user specific data is stored in /userdata, and the user is identified first by environment and then by name.
Data that is shared among users is stored in /PublicData. Cases that are intended to be shared by all users are stored in /PublicData, and organized per app. If data is to be shared per group, it is to be stored in /PublicData/groupname and there are no further restrictions.
Following this structure, the default access rights are predictable. So, all files created within a group folder get the access rights of that group folder, unless specified otherwise.
Uploading and Downloading Files
To detail the building blocks for the exchanging files between an AIMMS app and its environment, we need to distinguish two situations:
- For AIMMS WinUI apps
The client side of the AIMMS app runs on the client device itself. The app has direct access to the user files via the file and directory functions such as
FileCopyandFileDelete. See File and Directory Functions.
- For AIMMS WebUI apps
The app user interacts with the app via a Chrome Web browser, but the AIMMS app actually runs on the host of AIMMS Cloud. The AIMMS app has only direct access to the following files:
Those files that were packed in the corresponding
.aimmspackThose files that have been explicitly uploaded from the client computer that runs the Chrome Browser
Those files that have been explicitly downloaded from AIMMS PRO Storage
In a way, the second situation can be viewed as an extension of the first situation. We will detail the first situation first.
Exchanging Files for an AIMMS WinUI App
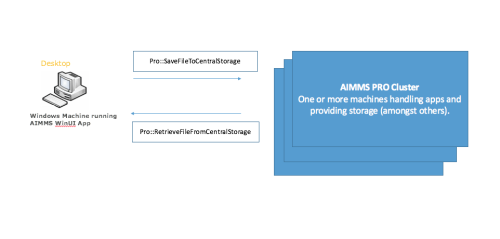
For WinUI apps you can exchange files with the functions pro::SaveFileToCentralStroage and pro::RetrieveFileFromCentralStorage. For example:
Pro::SaveFileToCentralStorage("c:\\Inputs\\data.txt", "pro:/PublicData/myapp/input/data.txt" );
This function will copy the file data.txt from the folder c:\inputs on the client Windows Desktop to the folder /PublicData/myapp/input in the AIMMS PRO Storage.
Note that Pro::SaveFileToCentralStorage requires the filename to be present in the second argument, and has a third optional argument to specify access rights for the file on the AIMMS PRO Storage. By default, a file inherits the access rights of the parent folder.
It is a good practice to check if the file already exists in AIMMS PRO Storage, so that you can warn the end-user when a file is about to be overwritten. You can do this with a self-defined procedure proFileExists as follows:
Procedure proFileExists {
Arguments: (spStoragePath);
Body: {
pro::NormalizeStoragePath(spStoragePath);
pro::SplitStoragePath(spStoragePath,spStorageBucketPath, spStorageFileWithoutPath);
ret := pro::storage::GetObjectInfo(spStorageBucketPath,
spStorageFileWithoutPath, tmpLocalFileName,
tmpType, tmpNum, tmpAuth, tmpVersion );
if ret = 0 or tmpNum <= 0 then
return 0 ;
endif ;
return 1 ;
}
StringParameter spStoragePath {
Property: Input;
}
StringParameter spStorageBucketPath;
StringParameter spStorageFileWithoutPath;
StringParameter tmpLocalFileName;
StringParameter tmpType;
Parameter tmpNum;
StringParameter tmpAuth;
Parameter tmpVersion;
Parameter ret;
}
There are also functions to create folders and to delete files and folders in the “Central Storage” section of the PRO API library AimmProLibrary.
Exchanging Files for an AIMMS WebUI App
In AIMMS WebUI apps, the end-user interaction is done in a Chrome browser on one machine, while the Client Side execution of AIMMS procedures is done on the host of AIMMS Cloud.
The file communication architecture for a WebUI AIMMS application is shown in the diagram below.
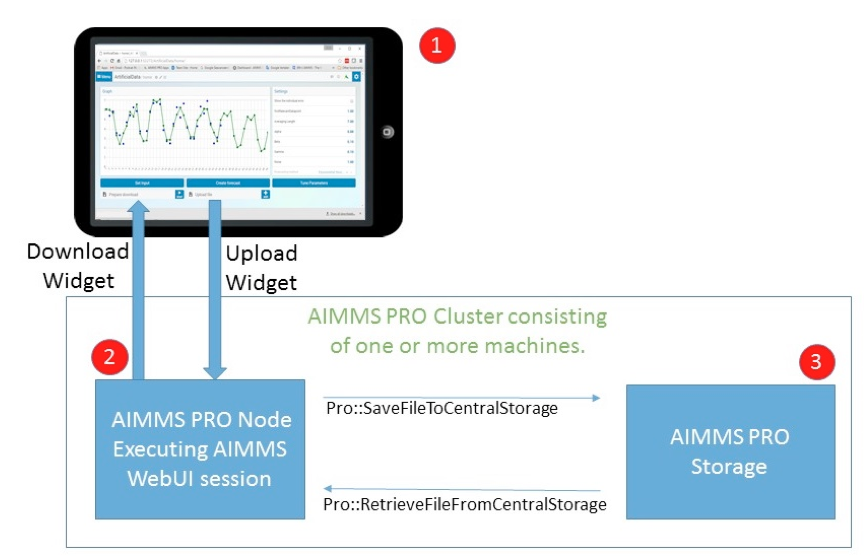
The Chrome Browser handles the interaction with the end-user. The Chrome browser can run on a device such as a smartphone, tablet, laptop, or desktop.
The AIMMS Client session running on the host of AIMMS Cloud. This AIMMS Client Session handles the execution of the statements in the model.
The AIMMS PRO Storage, disk space available to exchange files.
The AIMMS WebUI provides the Upload Widget to transfer files from your device to the folder in which the AIMMS client session runs. In addition, it provides the Download Widget to transfer files the other way around.
See also
Secure File Access: covers how to securely arrange file sharing.